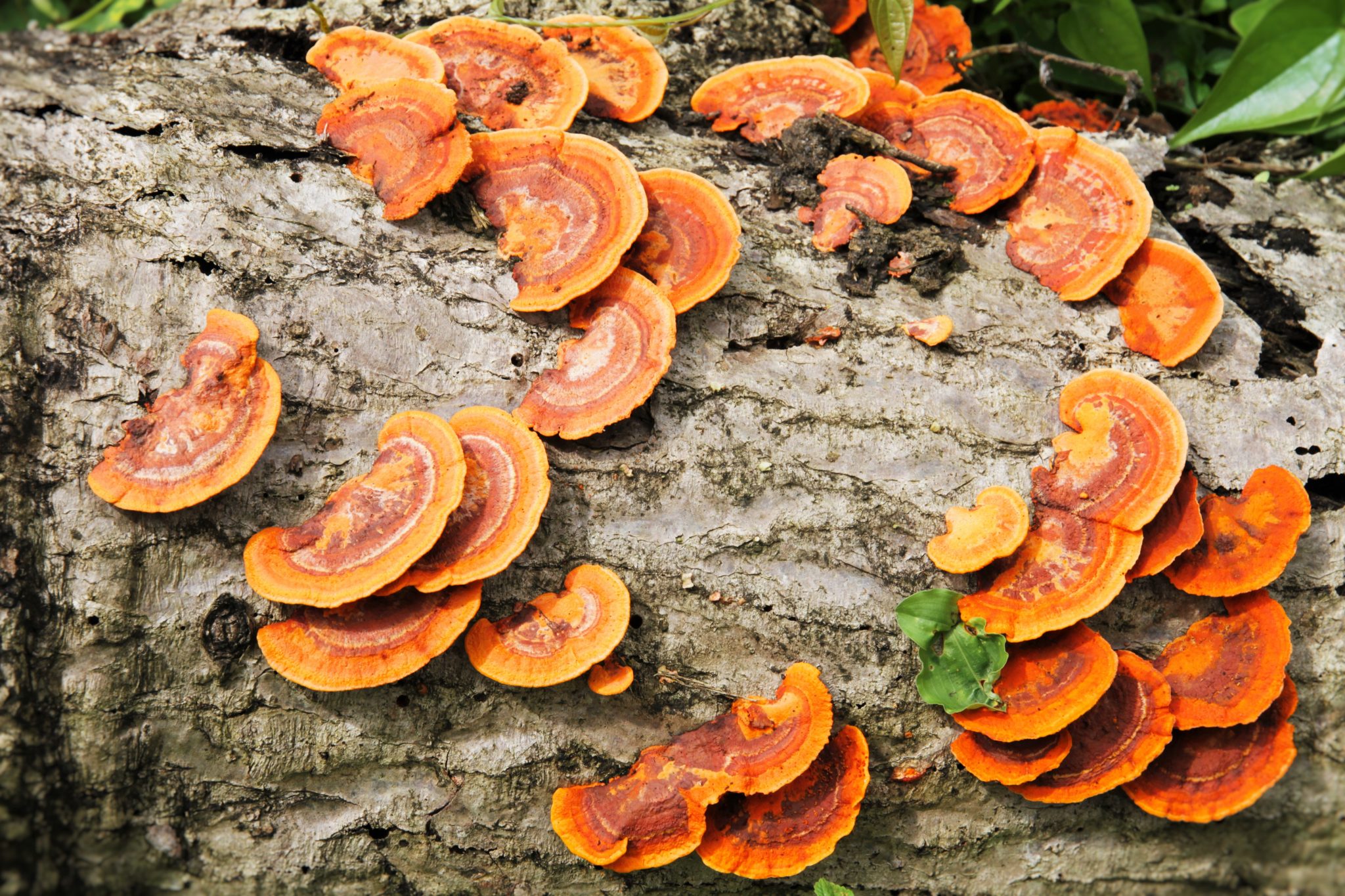
A New Recycling Method through Mushroom Biology Diagrams Mushrooms and Food Chains. In the context of food chains, mushrooms serve as both decomposers and primary consumers. As decomposers, they obtain energy and nutrients from dead or decaying materials, playing a critical role in the breakdown of organic matter. Mushrooms can be considered part of the food chain as both decomposers and primary

Fungi absorb nutrients from the plants and animals they consume while releasing enzymes that break down dead organic matter. Nutrient Cycling. Nutrient Cycling. Decomposers play a vital role in the food chain and give it a cyclical nature. Plants need sunlight and nutrients in the soil for photosynthesis, and decomposers are responsible for

These Are the Reasons Why Mushrooms Are Important to the Food Chain Biology Diagrams
Therefore, mushrooms are an essential part of the natural food chain as decomposers rather than producers. The Diet of Decomposers. The food of decomposers primarily consists of dead animals and plants, as well as the waste products of othr organisms.
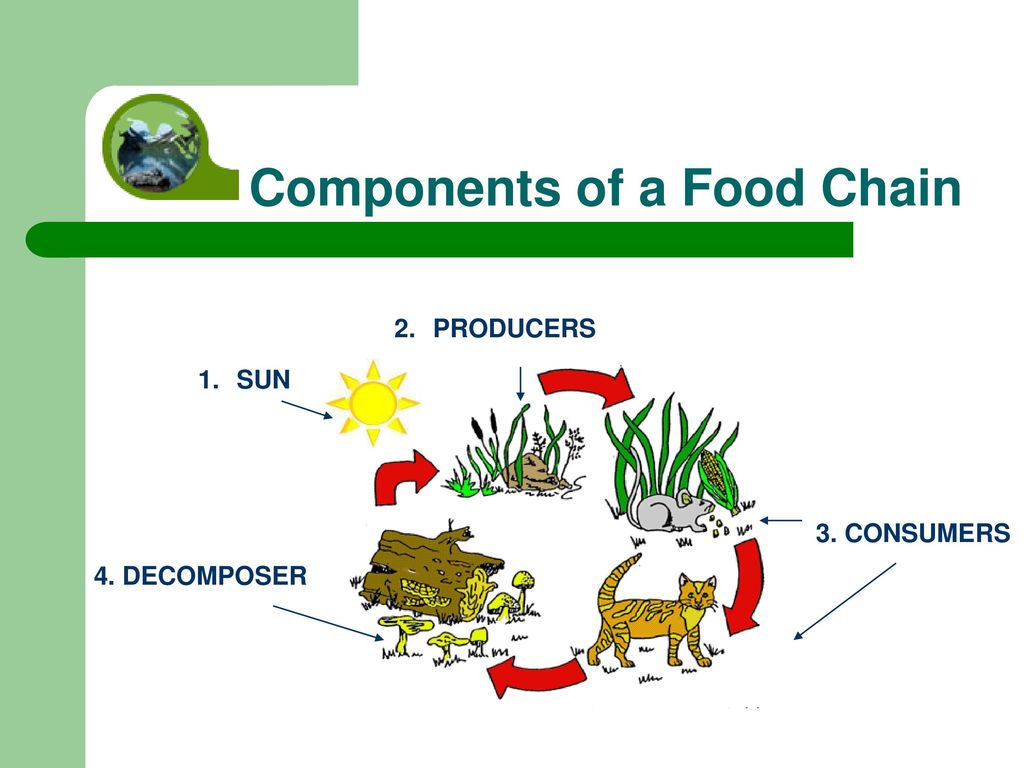
Mushrooms hold a significant position in the food chain as decomposers. They are part of the fungal kingdom and belong to the decomposer category, alongside various bacteria and fungi. Mushrooms play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler forms, thereby facilitating the recycling of nutrients.
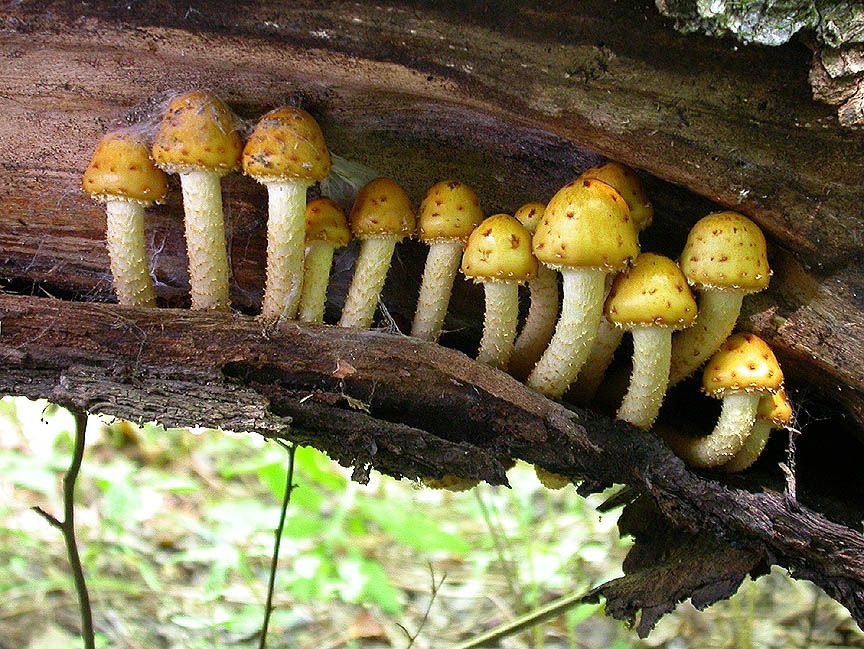

Definition, Parts, Types, and Examples Biology Diagrams
Fungi, including mushroom decomposers, are experts at nutrient recycling. They break down complex compounds into forms that can be readily used by other organisms. This means that nutrients remain accessible to plants, which, in turn, become part of the food chain. Mushrooms are decomposers that use dead and decaying material to gain energy and help to recycle nutrients back into the food chain and thus are essential to the food chain. Q.2. Why are food chains shorter at each trophic level? The final place in the food chain is occupied by decomposers such as fungi, which absorb dead organisms, such as dead plants and dead animal matter. Decomposition is a process in which decomposers break down dead organic matter and release inorganic material such as carbon dioxide and water, back to the soil, where producers can use it and
